BY David Lange, Director, Governance, Risk and Compliance Services, Weaver
BY David Lange, Director, Governance, Risk and Compliance Services, Weaver
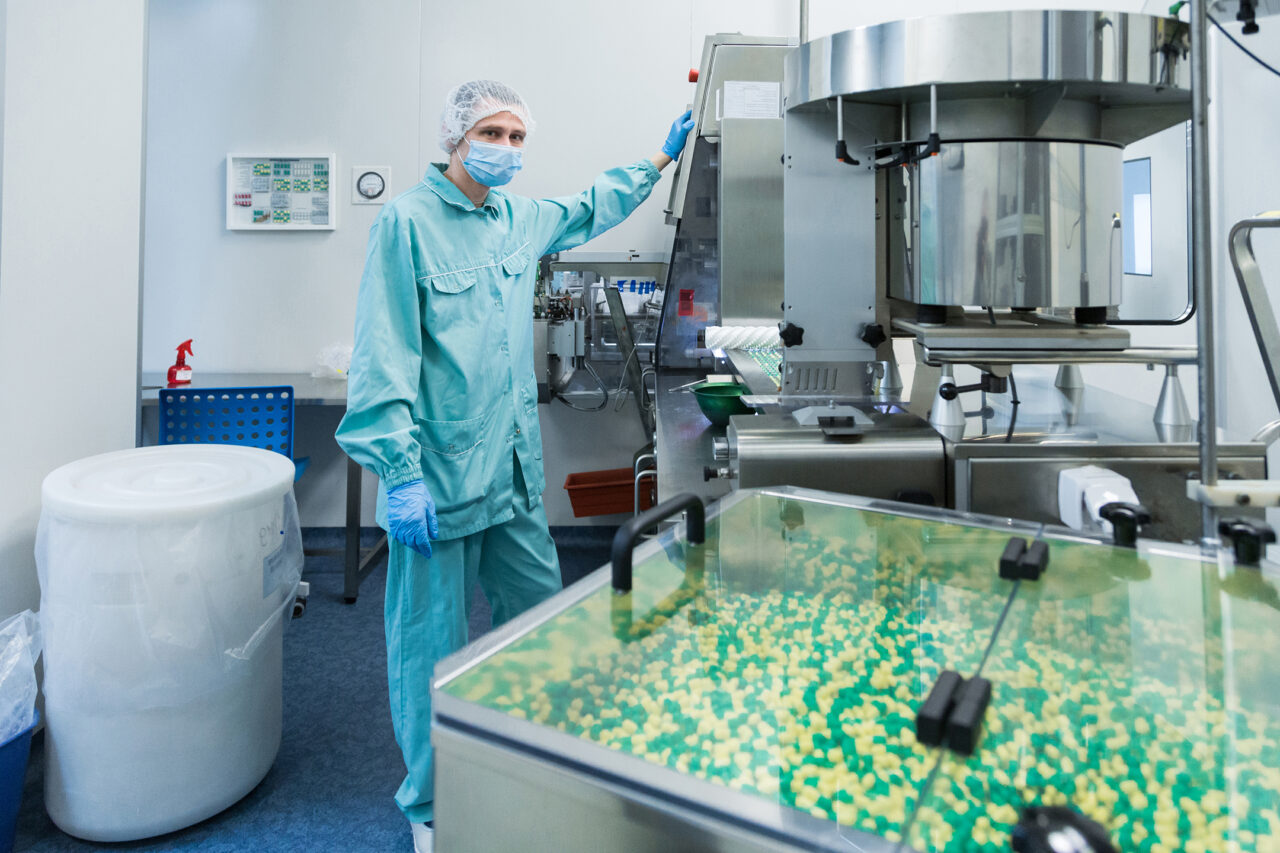
The pharmaceutical industry is undergoing a fundamental transformation in how drugs are manufactured. As regulatory requirements grow more complex and quality standards become increasingly stringent, companies are reevaluating their manufacturing strategies. The global pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market, projected to exceed $120 billion by 2025, reflects a growing trend toward outsourced manufacturing as a means to enhance quality, ensure compliance and optimize costs.
Current Manufacturing Landscape
The pharmaceutical manufacturing sector has undergone significant transformation in the last five years, with companies shifting from traditional single-site production models to multinode, digitally connected manufacturing networks that provide enhanced supply chain resilience and production flexibility.
Contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) have evolved significantly, developing sophisticated capabilities in specialized areas, such as biologics, cell and gene therapies and personalized medicine. Modern CMO facilities often feature advanced quality control systems, automated manufacturing processes and comprehensive regulatory compliance programs that match or exceed those of major pharmaceutical companies.
Recent industry data shows this evolution in action. Major pharmaceutical companies now outsource nearly 50% of their R&D activities, with even higher percentages among smaller companies — some reaching 100% outsourced manufacturing. This shift has driven the contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) market to approximately $140 billion as of 2023, reflecting the industry’s increasing reliance on external manufacturing partnerships.
These improvements in quality metrics are particularly noteworthy in complex manufacturing processes, such as sterile fill-finish operations and biological product manufacturing. Leading CMOs have achieved these results through significant investments in advanced quality control systems, automated inspection technologies and comprehensive staff training programs. The impact is evident in reduced batch rejection rates, improved process consistency and enhanced compliance with regulatory requirements across multiple jurisdictions.
The evolution of CMO capabilities has been particularly dramatic in emerging markets, where investments in state-of-the-art facilities and quality systems have created new options for pharmaceutical companies seeking to expand their manufacturing networks. These facilities often incorporate the latest quality control technologies and regulatory compliance systems, enabling them to meet or exceed the standards of established markets.
Future Outlook
The pharmaceutical manufacturing sector stands at the cusp of significant technological advancement. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing quality control processes, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time process optimization. Continuous manufacturing technologies are replacing traditional batch processes, offering improved consistency and quality control while reducing production costs. Industry examples include:
- Novartis: AI and machine learning for quality control in their manufacturing processes has increased efficiency by 15-20% and reduced downtime by approximately 30%.
- Pfizer: AI and machine learning optimization has cut deviations and quality issues by 25% in their production lines.
- Johnson & Johnson: Continuous manufacturing in Puerto Rico has reduced cycle times by 50% and decreased production costs by 70% compared to traditional batch manufacturing.
- Vertex Pharmaceuticals: Continuous manufacturing has boosted production capacity by 35% and lowered manufacturing costs by 40% for their cystic fibrosis drugs.
These technological advances are reshaping manufacturing strategy decisions. CMOs are often better positioned to invest in these advanced technologies, leveraging their scale to justify investments that might be prohibitive for individual pharmaceutical companies. This technological advantage is particularly evident in areas requiring specialized expertise or sophisticated quality control systems. For example, leading CMOs have implemented advanced process analytical technology (PAT) systems that enable real-time quality monitoring and control, representing investments of tens of millions of dollars that can be amortized across multiple clients and products.
The impact of these technological investments also extends beyond basic quality control. Advanced data analytics capabilities enable CMOs to identify subtle process trends and potential quality issues before they affect product quality. Automated inspection systems utilizing artificial intelligence can detect defects with greater accuracy and consistency than traditional methods. These capabilities not only improve product quality but also enhance manufacturing efficiency and reduce quality-related costs.
The regulatory landscape continues to evolve as well. Authorities worldwide are implementing more rigorous standards for data integrity, process validation and quality management systems. The FDA’s enhanced focus on data integrity and the European Union’s Medical Device Regulation (MDR) exemplify this trend toward more comprehensive quality requirements. These changes are driving many companies to reconsider their manufacturing strategies, particularly regarding quality control and regulatory compliance capabilities.
Benefits of Outsourced Manufacturing
The decision to outsource pharmaceutical manufacturing can offer significant advantages in quality control and regulatory compliance. Modern CMOs maintain sophisticated quality management systems that often exceed regulatory requirements across multiple jurisdictions. This comprehensive approach can provide pharmaceutical companies with enhanced quality capabilities without the need for substantial internal investment.
Financial benefits extend beyond direct cost savings. While traditional cost advantages such as reduced capital investment and lower operating expenses remain relevant, the financial impact of improved quality control and regulatory compliance can be equally significant. Industry data indicates that companies successfully leveraging CMO partnerships often achieve:
- 25-30% reduction in quality-related investigation costs
- 20-25% improvement in right-first-time manufacturing metrics
- 30-35% reduction in compliance-related capital expenditure
- Significant decreases in quality control staffing and training expenses
Access to specialized expertise represents another key benefit. Leading CMOs maintain teams of experts across various technical disciplines, providing pharmaceutical companies with capabilities that would be difficult or expensive to develop internally. This expertise becomes particularly valuable when dealing with complex products or challenging regulatory requirements, such as:
- Navigating global regulations: Different countries have varying regulatory requirements, and staying compliant with each jurisdiction’s regulations requires extensive knowledge and experience.
- Approval processes: The approval process for complex products, such as biologics and gene therapies, is often more stringent and requires detailed documentation and validation studies.
- Post-approval monitoring: Continuous monitoring and reporting are required even after product approval to ensure ongoing compliance and to manage any potential adverse effects.
Managing Manufacturing Risks
While outsourcing can enhance manufacturing capabilities, it also introduces risks that require careful management. Supply chain complexity represents a primary concern, particularly when working with multiple CMOs across different regions. Recent global disruptions, including the Trump administration’s talk on tariffs and the heavy reliance on Chinese manufacturing, have highlighted the need for robust supply chain oversight and effective contingency plans. Companies must diversify supply sources, enhance transparency and invest in technologies like blockchain and predictive analytics to mitigate risks and ensure resilience.
Quality control and regulatory compliance risks require particular attention. While CMOs generally maintain high standards, the pharmaceutical company retains ultimate responsibility for product quality and regulatory compliance. This reality necessitates maintaining effective oversight mechanisms and sufficient internal expertise to evaluate CMO performance properly.
Intellectual property protection presents another significant consideration. Sharing proprietary manufacturing processes with external partners requires careful attention to confidentiality agreements and technology transfer protocols. Companies must balance the benefits of outsourcing against the need to protect valuable intellectual property.
Several strategies have proven effective in managing these risks. Comprehensive CMO qualification programs help ensure partners maintain appropriate quality standards and compliance capabilities. These programs typically include detailed technical assessments, quality system evaluations and financial stability analysis. Regular audits and performance reviews enable early identification of potential issues, with leading companies implementing risk-based monitoring programs that adjust oversight intensity based on CMO performance and product criticality.
Clear quality agreements and well-defined performance metrics provide frameworks for maintaining consistent quality standards. These agreements often include specific requirements for process control, testing procedures and change management. Successfully implementing these control mechanisms requires significant attention to detail and ongoing commitment from both parties. Companies that excel in CMO management often establish dedicated teams responsible for oversight and relationship management, ensuring consistent focus on maintaining quality standards and regulatory compliance.
Moreover, effective risk management strategies increasingly incorporate advanced monitoring tools and data analytics capabilities. Real-time access to manufacturing and quality data enables pharmaceutical companies to maintain closer oversight of CMO operations and respond more quickly to potential issues. Some organizations have implemented sophisticated supplier scorecard systems that track multiple performance indicators, providing early warning of potential quality or compliance concerns.
For example, the Rx-360 Supplier Assessment Program is a widely used system in the pharmaceutical and biotech industries. It focuses on ensuring the quality and integrity of the supply chain by evaluating suppliers against rigorous standards. The system tracks multiple performance indicators, including:
- Quality management systems: Assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and adherence to good manufacturing practices (GMP)
- Regulatory compliance: Evaluation of the supplier’s compliance with regulatory requirements from agencies like the FDA, EMA and other global regulatory bodies
- Operational performance: Monitoring of the supplier’s delivery timelines, production capabilities and overall operational efficiency
- Risk management: Identification and mitigation of potential risks, including financial stability, geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions
- Sustainability and ethics: Assessment of the supplier’s commitment to environmental sustainability and ethical business practices
The program provides pharmaceutical companies with detailed scorecards and early warnings of potential quality or compliance concerns, enabling proactive management of their supply chains.
By leveraging such sophisticated supplier scorecard systems, pharmaceutical companies can enhance their supply chain oversight, ensuring that their products meet the highest standards of quality and safety.
Implementation Success Factors
Successful implementation of outsourced manufacturing strategies requires careful attention to several key factors. Effective technology transfer processes ensure smooth transitions of manufacturing operations while maintaining product quality. Clear communication channels and governance structures enable rapid response to quality issues or regulatory concerns.
Maintaining appropriate internal expertise remains crucial even in outsourced manufacturing relationships. While CMOs provide extensive capabilities, pharmaceutical companies must retain sufficient technical knowledge to effectively oversee operations and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
The pharmaceutical manufacturing landscape continues to evolve, driven by advancing technology, increasing regulatory requirements and growing quality expectations. Outsourced manufacturing offers significant potential benefits in quality control and regulatory compliance, alongside traditional cost advantages. However, realizing these benefits requires careful attention to risk management and effective oversight mechanisms. The most successful organizations approach outsourcing as a strategic initiative that requires ongoing attention and investment, rather than simply as a cost-reduction measure.
As quality standards continue to rise and regulatory requirements become more complex, the importance of selecting and managing manufacturing partners effectively becomes increasingly critical. Companies must develop comprehensive strategies that balance quality objectives, compliance requirements and operational efficiency. This includes maintaining appropriate internal expertise, implementing robust oversight mechanisms and fostering collaborative relationships with manufacturing partners.
Companies considering outsourced manufacturing must evaluate their specific circumstances, including product portfolio requirements, quality control needs and regulatory obligations. The most successful approaches typically combine clear quality objectives with robust oversight mechanisms, whether pursuing fully outsourced manufacturing or hybrid models.
In a cautionary tale, McNeil Consumer Healthcare, a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson, faced multiple recalls between 2009 and 2010 due to quality control issues at their Fort Washington, Pennsylvania plant. The recalls were related to contamination and improper manufacturing practices. As a result, the company was forced to address these failures when the FDA issued a consent decree requiring McNeil to improve its manufacturing processes. The fallout included more than 50 product recalls, financial losses exceeding $900 million and substantial reputational damage.
As the industry continues to evolve, manufacturing strategy decisions will increasingly focus on quality and compliance capabilities alongside traditional cost considerations. Organizations that effectively balance these factors while maintaining appropriate risk management controls will be best positioned for long-term success in an increasingly complex manufacturing environment.