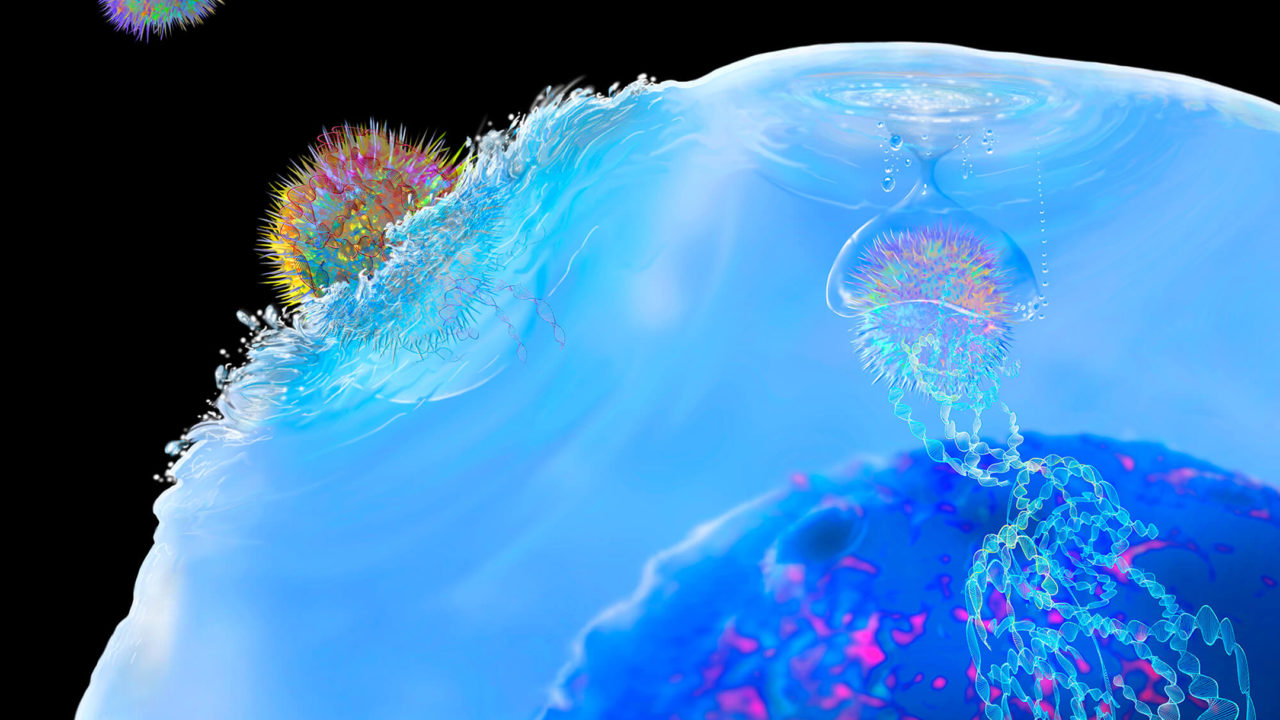
Researchers uncover mechanisms of protective antibody response during deadly Marburg virus infection
A detailed study of the monoclonal antibodies from a person who survived a Marburg infection led researchers to identify novel mechanisms that contribute protection against the disease, according to the latest findings of a collaborative team led by The University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston and Vanderbilt University Medical Center. Certainly, the virus that is on everyone’s mind is the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 that causes COVID-19 disease, but there are other viral families that continue...

![Using telemedicine during COVID19 may perpetuate health disparities in Harris County [Opinion]](https://mjhnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/telemedicine.png)